Your business is the result of a lot of hard work. Wether it's the big amount of money you need to open your doors or the hours you spent making your business profitable, you need to now protect that investment.
It can be hard to understand commercial insurance. Your choices about what to buy or not to buy are almost endless. You can better control the risk in your business and save money on coverage you may not really need if you know the basics of commercial insurance 101.
We should first talk about why companies of all sizes buy insurance before we get into the basics of business insurance.
Having commercial insurance protects your capital and business from things that could destroy them. It is very important to protect both your belongings and your liability for harm you cause to other people.
A lot of people who buy industrial insurance for the first time do so because their businesses are now at a point where they are vulnerable to risk. They may have valuable goods that need to be protected, or the government, their customers, the bank, or their landlords may require them to have insurance in order to run their business.
Many businesses lean on insurance software solutions to minimize the manual leg work.
Commercial insurance is usually a one-year deal that says the insurance company will take on your business's debts in exchange for a set amount of money at the start of the policy term.
Most of the time, this amount is based on how much land you own or how much debt you have. Most of the time, the limits are set by the rules that your landlord, suppliers, or project partners want you to follow.
Insurance Agency Management Software helps in managing different insurance responsibilities for insurance agencies.
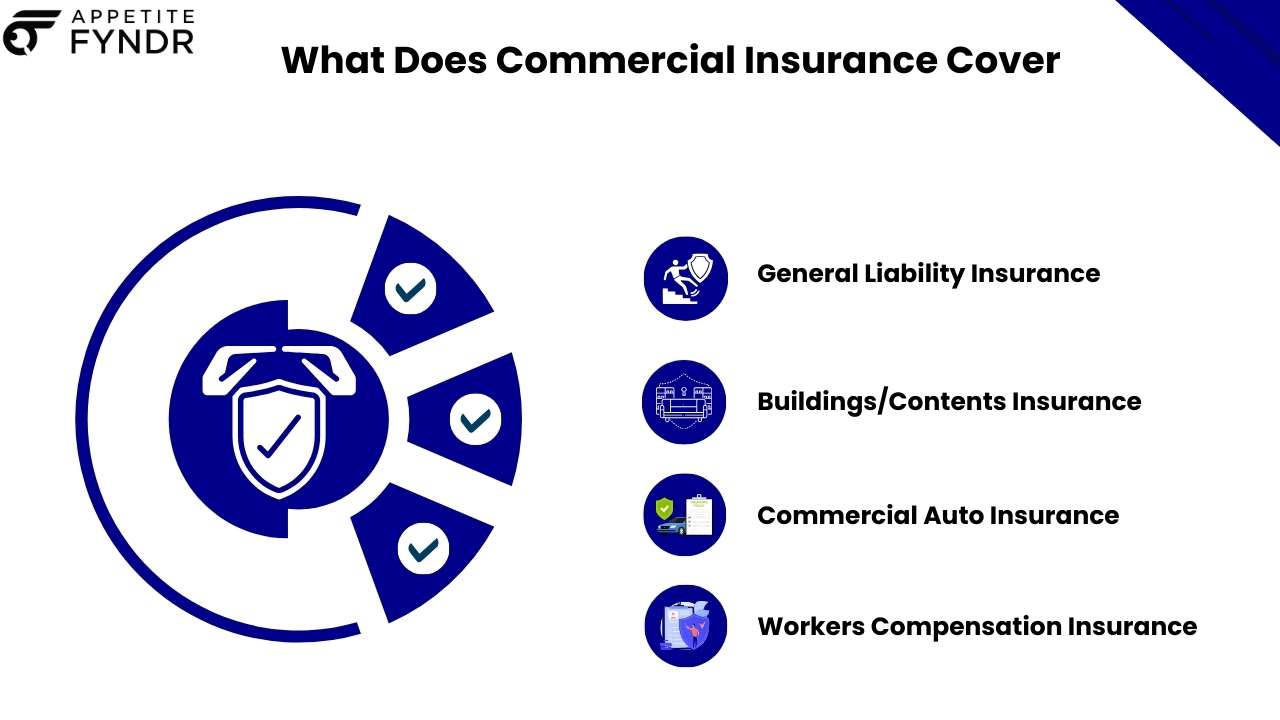
Each business is different and needs a different kind of protection. Out of these facts about business insurance, there are four policies that you should buy or will probably need to buy at some point.
General liability insurance covers injuries or damage to other people's property that you cause while running your business. This keeps you safe from injuries like slips and falls, product responsibility, and other costs.
This insurance covers not only the damage you cause, but also the costs of defending you in court and settling claims. If the claim falls under one of these categories, commercial general liability coverage will also cover and pay for defense costs associated with any frivolous lawsuits that arise against your business.
General Liability covers several categories of claims; three key ones should be familiar:
Because every business is different, you should always talk to an insurance expert to figure out what coverages you need and don't need. But remember that every business and charity should have at least a general liability policy. This is one of the most important things to keep in mind as you learn about commercial insurance.
When you have commercial property insurance, your belongings are protected against direct damage. This includes the building itself, its belongings, and the area around it. Your property should also be insured while it's off-site or in transit, to provide further security for it and you. More specifically, this policy covers:
If a bank financed the building, you may have to have commercial property insurance. However, most business owners choose to buy coverage to protect their investment. A business owner should think about how important the property is to their business and how easy it would be to replace it if something bad happened.
You will need professional auto insurance if you use or own cars for your business. This coverage protects you from any liability that comes with driving the car and any damage you cause to it.
State law says that if your business owns cars, you need to have commercial auto insurance.
If you run a business, you are likely responsible for the people who work for you. If these workers get hurt while doing the work you told them to do, you have to pay for their medical bills and time off work. Depending on how bad the accident was, these hospital bills can get very expensive. Workers' compensation coverage provides medical bills coverage as well as income replacement during periods of disability for injured employees.
In most states, you need this coverage if you have workers who aren't related to you or own the business. Also, this coverage is bought through private insurance companies in most states. However, in Ohio, North Dakota, Washington, Wyoming and Puerto Rico/USVI workers' compensation payments must be made through state funds.
Don't forget that you might need to get workers' compensation insurance even if you think all of your staff are self-employed. In short, your state has rules that say how to classify employees and whether the company paying the bills has to cover them with workers' compensation insurance. It doesn't matter what you call the person who works for you. As an example, if you tell someone when they can and cannot work, what tools they must use, or how they must do their job, that person is probably an employee and not an independent worker.
This is a very complicated subject that business owners often find hard to understand. To find out if you need this coverage, you should talk to an insurance expert about your specific case.
The word "commercial risk" or "business risk" refers to a number of dangers that can hinder the success of a business. These business risks can also put a company in the red or even cause it to shut down if they are not kept in check. This is why it's important to handle risks well.
The following are some cases of commercial risk:
These risks can sometimes happen at the same time. A data breach is an example of a security risk that can make people not trust your business, which is an image risk.
Another example is if there is an accident (an operational risk) and it turns out that your company wasn't following safety rules (a compliance risk).
It's possible that business risks can't be completely removed. Because of this, one of the most popular forms of risk management includes four different ways to deal with known risks:
A lot of the time, businesses decide how to handle their economic risks. As an example, these days, problems with your image can spread like wildfire on social media. This means that most businesses are open to image risks, even if they don't have a social media account. A business can choose to do the following in this case:
In other situations, there are only set ways to deal with a business risk. It does this because not all risks can be insured. For these kinds of risks, the ability to transfer the risk may be restricted or not possible at all.
When it comes to economic risks, some examples of business risks are changing interest rates, recession, inflation, taxes, and so on. Most business risk insurance policies don't cover these huge changes.
Depending on the type of business, there are different rules and laws that must be followed. Most of the time, people who don't follow the rules get fined or punished because they are breaking the law. As a result, there is no type of business risk insurance that covers compliance threats.
Professional liability insurance, also called professional indemnity insurance, is the most similar type of business risk insurance that can shield you from this risk. This type of insurance, on the other hand, only covers mistakes, lapses, and carelessness that were not meant to happen. This means that when it comes to professional liability insurance, legal risks are still not clear.
At the end of the day, lowering legal risks is the best thing to do. You can do this by keeping up with new rules, checking your business's processes for compliance on a regular basis, or hiring a consultant to do the job.
This is one type of business danger that can't be covered by insurance. Getting rid of this risk is the best thing that can be done. Taking a close look at your company's plan, making your business model better, and most importantly, listening to what your customers say can help lower this risk.
There isn't always commercial risk insurance that can protect a business's image. But if a cybercrime (like a data breach) hurts your company's image, some cyber liability insurance plans will pay for the lost profit.
Business risk insurance comes in a few different types that cover security threats. One example is cyber liability insurance, which keeps companies safe from all types of hacking.
Crime insurance or loyalty insurance is another example. These types of insurance protect against theft, fraud, forgery, embezzlement, and so on.
If you have the right kind of insurance, your business can keep running even if something goes wrong with your vehicles, your equipment breaks down, your tools and materials get damaged, and so on. Commercial risk insurance can also ensure income even if a business can't run because of damage to or inaccessibility of property. This is a risk that comes with business property insurance.
Some unplanned events are covered by all insurance, but scalable insurance plans are the most adaptable. Insurance that can be scaled up or down can adapt to the needs of your business as they change. For instance, you might be able to change your plan if your team gets smaller or if a global disease makes you less productive. Before committing to a covering choice, make sure that it can be expanded.
When you think about how much insurance costs, pay close attention to how much it costs each employee. Find out how much each employee makes and how much their pay cost. Your business insurance (or the health insurance you give your workers) shouldn't cost a lot more than the average amount of money you make from each employee. If the cost of coverage per employee is a lot more than what they make, you'll quickly go into the red.
Some people worry about how much insurance costs, but in the long run, it can save you a lot of money in case settlements. When you compare prices and benefits, make sure you don't lower the quality of the coverage to save money. Choose coverage that fits your budget and stick with companies you can trust.
Workers' compensation insurance is something you need if you have staff. A lot of the time, landlords make tenants get a general liability insurance policy to protect them from claims for injuries or damage to their property. Some clients may demand that you have a certain kind of insurance before they hire you. Someone who works in insurance can help you find out what you need for your state and business.
There are different risks in each industry. When you work as an expert in a field like accounting or coaching, you should get professional liability insurance. If they make a mistake, the insurance helps pay for it. Businesses that sell things, like stores and restaurants, are better off with product liability. It can cover broken things or food that makes you sick. When you look for insurance, think about the risks you face in your job.
Business insurance plans usually have a deductible that you need to pay before the insurance company starts to pay your bills. This is similar to how most health insurance plans work. When you raise your deductible, your premiums go down. When picking a plan, you should think about how much the payment and deductible will cost. If you want lower rates, don't choose a plan with a high deductible that you can't pay.
It's possible that your business will need more than one set of rules to be fully covered. A small business might have a business owner's policy, which covers general liability and property damage. It might also have business interruption insurance for things like fires and floods, errors and omissions insurance for professional liability, product liability insurance for stores and restaurants that sell goods, cyber insurance to protect data and technology, and auto insurance if it has any vehicles.
You should think about all of your insurance choices and how well each one is rated by professionals. People know that providers with good ratings will pay on time and offer consistent service. Find out about the different kinds of insurance to see which ones might apply to your business. In a spreadsheet, you can list all of your choices and compare their fees and what they cover. This work will pay off in the long run, so put in the time.
Get quotes from several service companies before making your final choice, just like you would with any other business decision. Your rate will depend on things like the size of your business, where it's located, and the assets you want to cover. Give all possible companies the same information. Once you have your quotes, get rid of any prices that are too low or too high and then figure out what the real price range is.
Getting quotes is also an important step for making sure that your budget and the cost of your insurance are in line with each other. You may need to make some changes to your budget in order to afford the coverage you need. Your rates might be a bit high. To lower your risk and your rates, you can make changes like installing fire control systems or making your workplace safer.
Some people choose the most basic general liability plan because it is the cheapest, but you can find a better one that fits your business's needs that won't cost much more. Make a list of your risks, including problems you've already had and problems you think you might have in the future. Does your business use big tools? Do you use cars to get your services or goods to customers? Talk to any trusted teachers or contacts you have in the field. They may have different experiences or insights that can help you figure out how much risk you are taking.
You should get more insurance than you need just to be safe. Then, you can compare your list of risks to the different coverage choices to find the one that fits you best. A meeting with an experienced insurance agent can help you find the best choice if you're having trouble.
Every company with employees is required by the federal government to have workers' compensation, unemployment, and disability insurance. And after that, you should carefully look over the legal requirements for your business in your state and field. It should be possible to find the Division of Insurance or a similar office on the website for your state, along with a list of insurance requirements.
If you need help from an insurance agent, try to talk to someone from your state. Agents may also specialize in a certain field. Finding one who knows a lot about yours would give you the best advice for your situation. Once you've chosen the insurance plans you need, you'll have a better idea of what coverage gaps you still have and how to best fill them with other plans.
Your insurance needs will change as your business does. You should look over your insurance benefits and costs every year to make sure they match what you need now or what you think you will need soon. Get in touch with your provider to find out how adding more space or new tools will affect your coverage.
Do not forget to make plans for when you can no longer run the business, even if it is an emergency. A review once a year is also a good time to get rid of any coverage you don't need. This will free up money that you can put toward better coverage.
Finding out what kinds of business insurance your company does and does not need is an important first step. Some of the most popular types of business insurance are these:
Conclusion:
Having the right commercial insurance is vital for safeguarding your business from unexpected risks and liabilities. By choosing the right coverage, you not only protect your physical assets but also ensure the continuity and resilience of your operations.
Explore Appetite Fyndr, the leading marketplace connecting insurance agents and carriers, and find the perfect coverage for your business today! Sign up for our platform and get connected to your target carriers and agents.